http://edition.cnn.com/2015/07/17/world/egyptian-child-mummies/index.html
Tag Archives: mummy
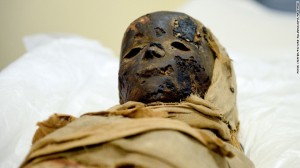
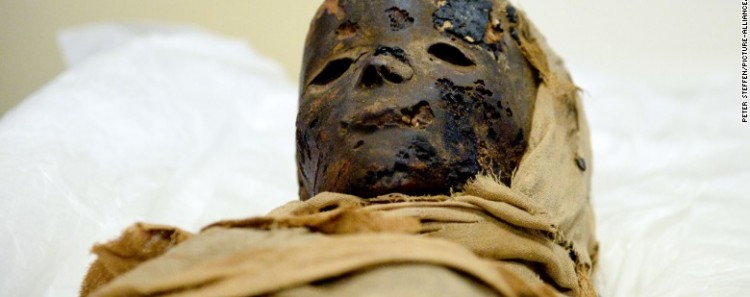
The secrets of Egyptian child mummies…
- Wednesday, 22 July 2015 11:56
- 0 Comments
Archaeologists help restore the mummy of a village chief.
- Thursday, 28 May 2015 15:08
- 0 Comments

Most people think archaeologists spend all their time hip-deep in pits excavating, but much of what archaeologists do is modern preservation work. In this case, the archaeologists travelled to Papua New Guinea to help local villagers patch up the mummy. For example, crushed Suca shell has the pH of bleach and helped keep lichen from growing on the mummy. The Anga people consult with their mummified ancestors to ask advice. Hopefully, archaeologists can help them protect their ancestors so this ancient practice may continue. READ MORE:
http://www.livescience.com/50948-photos-smoked-mummies-papua-new-guinea.html